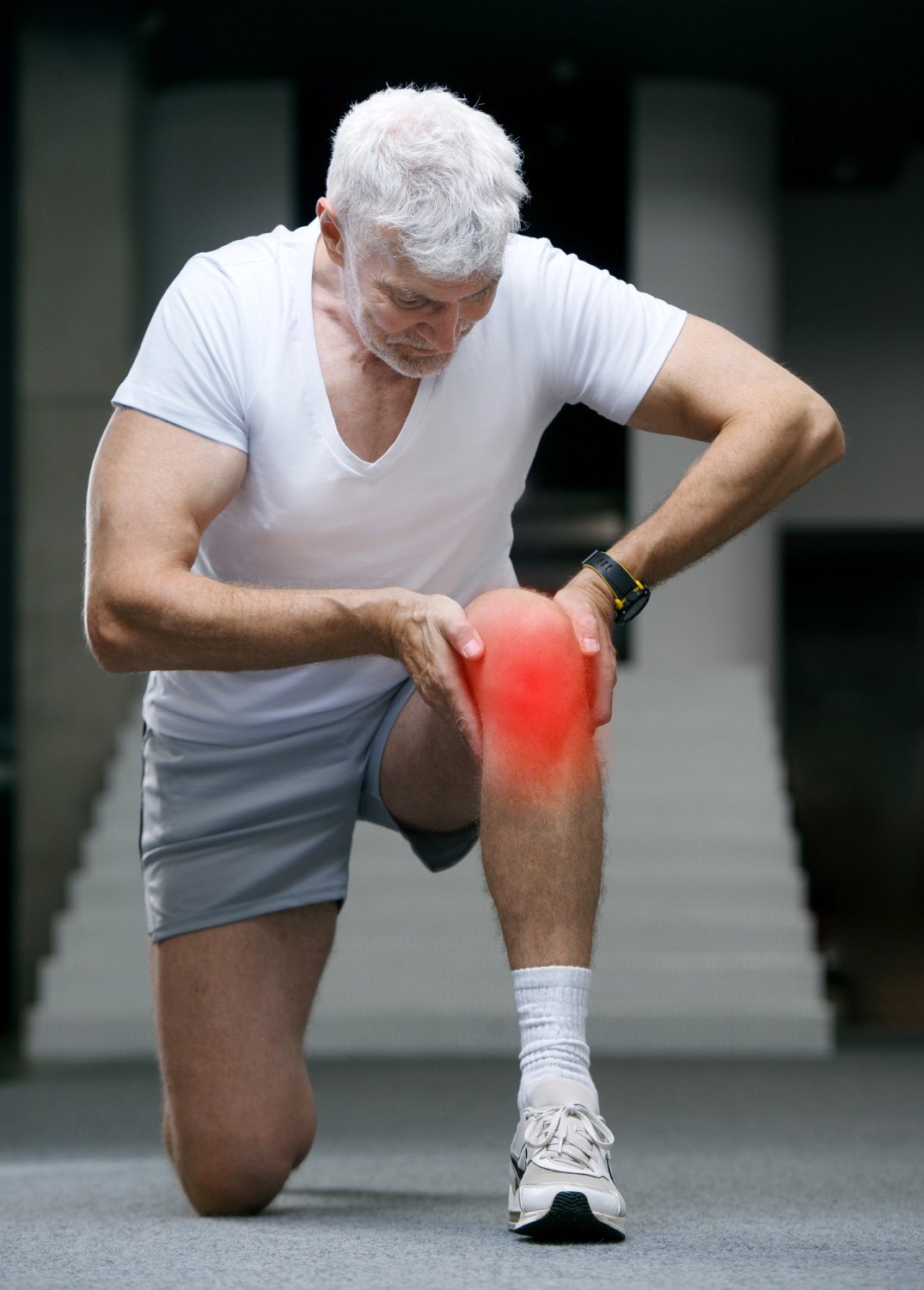
Knee Pain
Your knee, the body’s largest joint, is crucial for movement. Cartilage cushions and protects bones during movement. When this cartilage breaks down due to injury, aging, or arthritis, pain arises.
Causes of knee pain
Osteoarthritis (OA): This “wear-and-tear” arthritis gradually destroys knee cartilage, often affecting overweight individuals or those with previous injuries. Symptoms include pain, stiffness, and limited movement.
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA): Unlike OA, RA is an autoimmune disease that attacks healthy joints. It can cause joint inflammation, swelling, and pain in both knees.
Bursitis: Inflammation of the fluid-filled sacs ( bursae) surrounding the knee, often caused by repetitive motions or kneeling.
Tendonitis: Overuse can inflame the tendons connecting muscles to bones in the knee. Patellar tendinitis (jumper’s knee) is a common example.
Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome (PFPS): This causes pain around the kneecap due to improper tracking, overuse, or weak muscles. Symptoms include pain while climbing stairs or squatting.
Injuries: Sports injuries, falls, or trauma can damage ligaments that stabilize the knee joint.
Other Services
Diagnosis
Diagnosis involves a detailed medical history and physical examination to pinpoint the pain location, severity, and aggravating/relieving factors. Imaging tests like X-rays, MRIs, or CT scans may be used for further evaluation.
Treatment Options
Many knee pain cases can be managed conservatively:
Rest: Reduce stress on the joint by resting the knee, especially after injuries or inflammation.f ineffective, consult a pain specialist for further evaluation.
Ice/Heat Therapy: Apply ice packs to reduce inflammation and swelling, followed by heat therapy to improve flexibility.
Pain Relievers: Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or naproxen can help manage pain.
Weight Management: Reducing weight lessens pressure on the knees.
Bracing:
Knee braces support and stabilize the joint, particularly when ligaments are weak.
Injections
Corticosteroid injections: Potent anti-inflammatory medications injected into the knee to reduce pain and inflammation.
Viscosupplementation: Injection of a lubricant into the joint to improve cushioning and ease friction.
PRP Therapy: Platelet-rich plasma, derived from the patient’s blood, is injected to promote healing in damaged tendons or cartilage.
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy exercises strengthen muscles surrounding the knee joint, improve stability and flexibility, and reduce pain.
Surgery
In severe OA, RA, or ligament injuries, surgery may be considered. Options include partial or total knee replacements or arthroscopic/open repairs for ligament tears.
-
Varied Range of Pain Conditions.
Patient Testimonials
-
I never realized how much my posture was affecting my overall health until I started seeing a Pain Management Specialist They've helped me improve my posture and as a result, I feel more confident and less fatigued.
-
I was skeptical at first, but Dr. Pritam Sir and his team really knew what they were doing. They listened to my concerns and tailored a treatment plan that worked specifically for me. Now, I'm pain-free and have more energy than ever.
-
Spinex has been a game-changer for me. I used to rely on pain medication to get through the day, but now I don't need it anymore. Dr. Pritam has helped me take control of my health and live a happier, more active life.